Maven repositories can be configured as an external feed, allowing the artifacts contained in the repository to be consumed by the Octopus steps that deploy Java packages, as well as the generic Transfer a package step.
Adding an external Maven feed
The following steps can be followed to add an external Maven feed.
- Select Library ➜ External feeds and click the ADD FEED button.
- Select Maven Feed from the Feed Type field.
- Enter the name of the feed in the Feed name field.
- In the Feed url field, enter the URL of the Maven feed. The URL must point to the directory under which the initial directory that makes up the Maven artifact group ids are found. For example, for the Maven central repo the URL is
https://repo.maven.apache.org/maven2and the SonaType Snapshot repo URL ishttps://oss.sonatype.org/content/repositories/snapshots. - If the Maven repository is password protected, the credentials can be entered into the Feed login and Feed password field.
- The *Download attempts (attempts)* field defines the number of times that Octopus will attempt to download an artifact from a Maven repository. Failed attempts will wait for the number of seconds defined in the Download retry backoff (seconds) field before attempting to download the artifact again.
When configuring external Maven repositories, we need to link to the repository itself and not the services that are used to search the repositories. For example URLs like https://search.maven.org/ or https://mvnrepository.com/ can’t be entered because these are sites for searching the repositories, and not the repositories themselves.
Referencing Maven artifacts
When referencing a Maven artifact, the package ID is in the format group:artifact.
For example, to reference the Maven artifact with the group of org.wildfly.swarm.testsuite and artifact of testsuite-https (i.e. the artifacts found at https://repo.maven.apache.org/maven2/org/wildfly/swarm/testsuite/testsuite-https/), you would enter a package ID of org.wildfly.swarm.testsuite:testsuite-https.
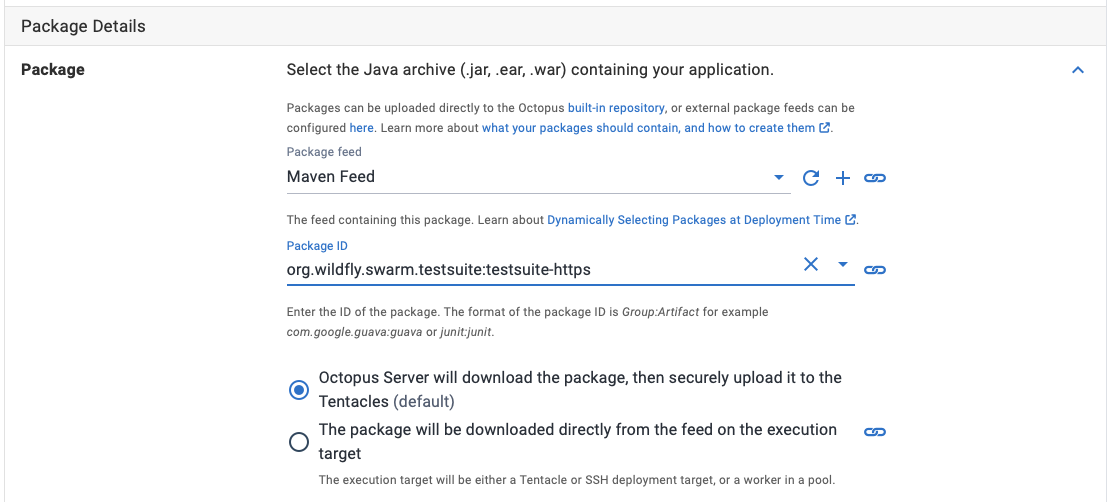
Prior to 2020.3.0, the packaging type is determined automatically from the extensions supported by Octopus, which are:
- zip
- jar
- ear
- rar
- war
So the package ID org.wildfly.swarm.testsuite:testsuite-https for version 2017.10.0 would download the WAR file https://repo.maven.apache.org/maven2/org/wildfly/swarm/testsuite/testsuite-https/2017.10.0/testsuite-https-2017.10.0.war.
Since 2020.3.0, Maven artifacts can be specified with an optional packaging and classifier. For example, the artifact ID of org.example:myartifact:zip will select the ZIP package with the group org.example and the artifact ID of myartifact, or org.example:myartifact:jar:sources will select the JAR package with the sources classification.
The packaging must be defined when using a classifier.
If no packaging selection is specified, the first matching package is selected from the list of extensions above.
Searching for Maven artifacts
As Maven repositories do not expose an API (repositories are just a filesystem structure), there is no way to search them in Octopus the way you might search a NuGet repository. The package ID for a Maven artifact must be complete for Octopus to identify it, and partial package IDs will not return a list of partial matches.
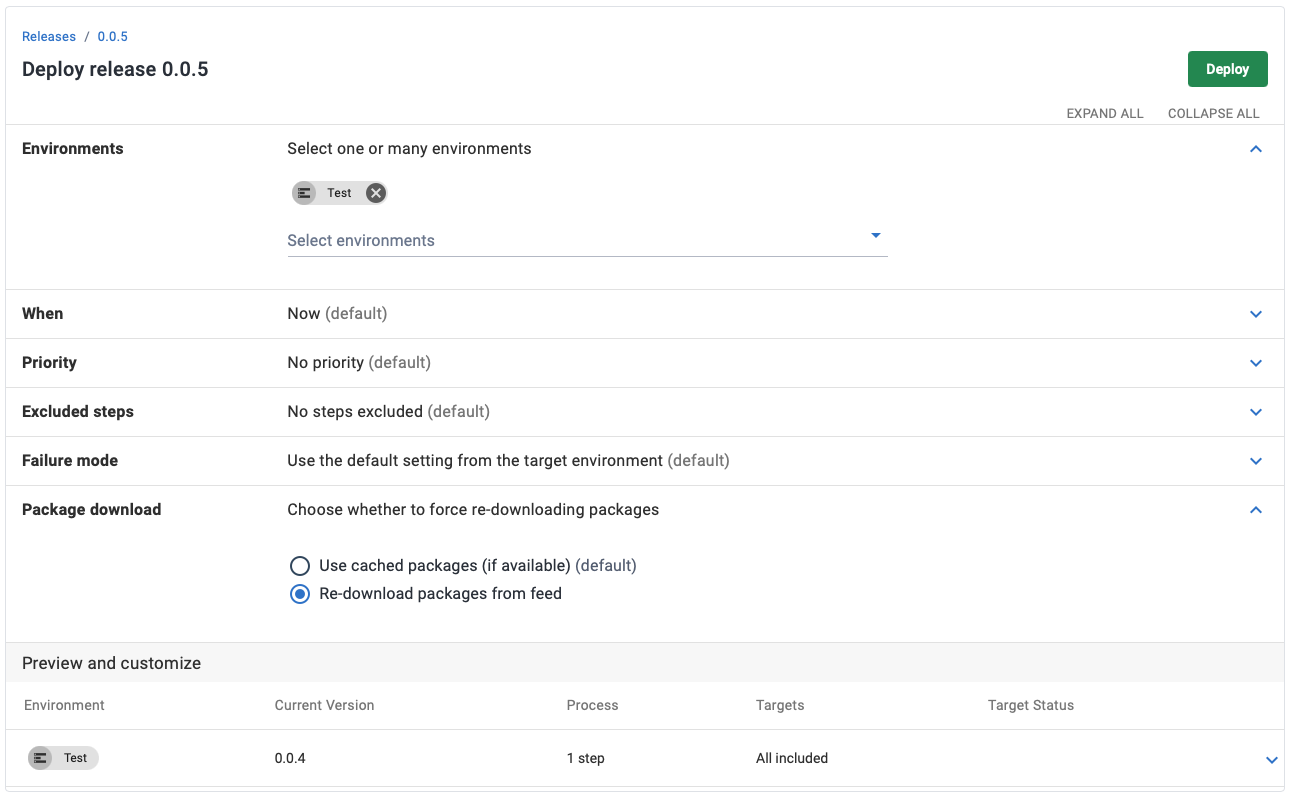
Downloading SNAPSHOT releases
When downloading SNAPSHOT releases of Maven artifacts, the latest SNAPSHOT version will be downloaded. This version is then saved in the Octopus cache, and will be reused in subsequent deployments of the same SNAPSHOT version.
What this means is that if a new SNAPSHOT artifact is published to the Maven repository after Octopus has saved the previous SNAPSHOT artifact to its local cache, Octopus will continue to use the older locally cached version.
To force Octopus to download the newer SNAPSHOT release, select the Re-download packages from feed option when deploying.
Versioning with Maven feeds
When using artifacts from a Maven feed, the Maven versioning scheme is used.
The following qualifiers in the version are used to indicate that it is a pre-release version:
alpha(or theashorthand) e.g.1.0.0-alpha1or1.0.0-a1.beta(or thebshorthand) e.g.1.0.0-beta1or1.0.0-b1.milestone(or themshorthand) e.g.1.0.0-milestone1or1.0.0-m1.rcorcre.g.1.0.0-rc1or1.0.0-cr1.SHAPSHOTe.g.1.0.0-SNAPSHOT.
Version ranges with Maven feeds
When defining versions ranges against artifacts sourced from a Maven feed (when defining a channel rule for example), the Maven range specification is used. The table below shows some common examples of Maven version ranges.
| Range | Meaning |
|---|---|
| 1.0 | x >= 1.0 * The default Maven meaning for 1.0 is everything (,) but with 1.0 recommended. Obviously this doesn’t work for enforcing versions here, so it has been redefined as a minimum version. |
| (,1.0] | x <= 1.0 |
| (,1.0) | x < 1.0 |
| [1.0] | x == 1.0 |
| [1.0,) | x >= 1.0 |
| (1.0,) | x > 1.0 |
| (1.0,2.0) | 1.0 < x < 2.0 |
| [1.0,2.0] | 1.0 <= x <= 2.0 |
| (,1.0],[1.2,) | x <= 1.0 or x >= 1.2. Multiple sets are comma-separated |
| (,1.1),(1.1,) | x != 1.1 |
Troubleshooting Maven feeds
- Can you download the POM file directly from the Maven repository from the Octopus Server? For example, the Google Guava POM file for version 24.0-jre is https://repo.maven.apache.org/maven2/com/google/guava/guava/24.0-jre/guava-24.0-jre.pom. If you can not, then there is likely to be an issue with the URL or your network settings.
- The Maven URL to be configured in Octopus includes the path up to the to the start of the group id. For Guava, the group id is
com.google.guava. This maps to thecom/google/guavacomponent of the URL. So the Maven URL to be configured in Octopus is https://repo.maven.apache.org/maven2/, because this is the part of the URL that does not include the group id. - Maven artifacts must be referenced in the
group:artifactformat. For Guava, the group iscom.google.guavaand the artifact isguava. So this would be referenced in Octopus ascom.google.guava:guava.
Help us continuously improve
Please let us know if you have any feedback about this page.
Page updated on Sunday, January 1, 2023