Helm Charts are like a package manager for Kubernetes applications, allowing users to reuse and share complex resource configurations.
Helm chart sources
You can source your Helm charts from two different sources:
- Packages from Helm or OCI feeds
- Git Repository
Helm feed
A Helm Feed in Octopus refers to a Helm Chart repository. This repository is effectively just an HTTP server that houses an index.yaml which describes the charts available on that server. Octopus uses this index file to determine the available “packages” (Charts) and versions. A chart is a tarball that looks like alpine-0.1.2.tgz which for this example Octopus will interpret as having PackageID alpine and version 0.1.2. There are various ways you can host a chart repository, including third-party tools like ChartMuseum, Artifactory, Cloudsmith, or even hosting your own static web server.
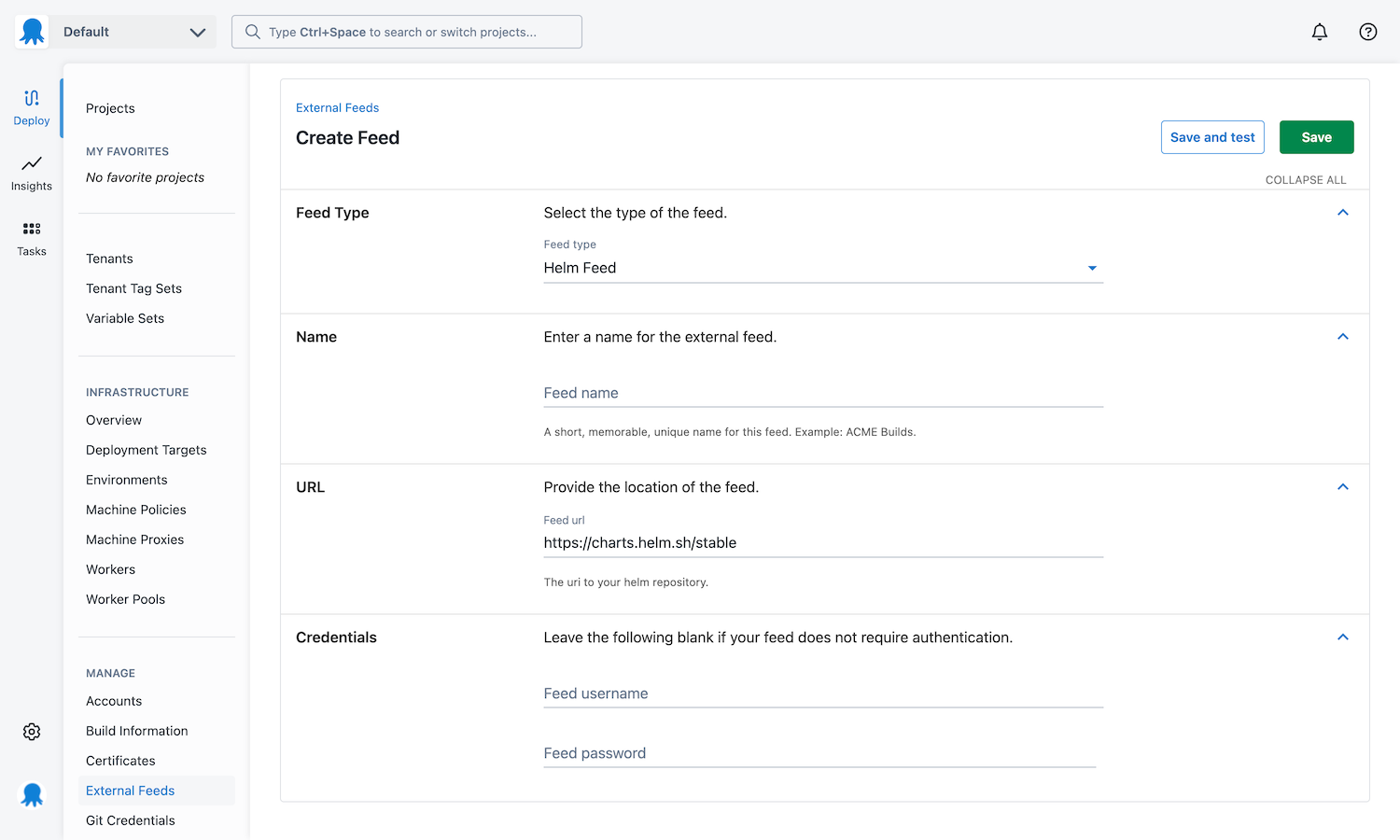
The built-in repository is capable of storing Helm Charts. However, the mechanism for determining the PackageID and Version may differ depending on the contents of the .tgz file. If the .tgz file contains a chart.yaml file, the PackageID is determined by the name, and the version is determined by the version sections of the YAML.
apiVersion: v2
name: petclinic-chart
description: A Helm chart for Kubernetes
type: application
version: 1.0.0
appVersion: "1.16.0"If the .tgz does not have a chart.yaml file, the PackageID and version are interpreted by the filename as described above.
For more information about Helm Chart repositories and how to run your own private repository, check out the living documentation on their GitHub repo.
OCI-based registry feed
The Open Container Initiative (OCI) is a lightweight, open governance structure (project), formed under the auspices of the Linux Foundation, for the express purpose of creating open industry standards around container formats and runtimes
An OCI-based registry can contain zero or more Helm repositories and each of those repositories can contain zero or more packaged Helm charts.
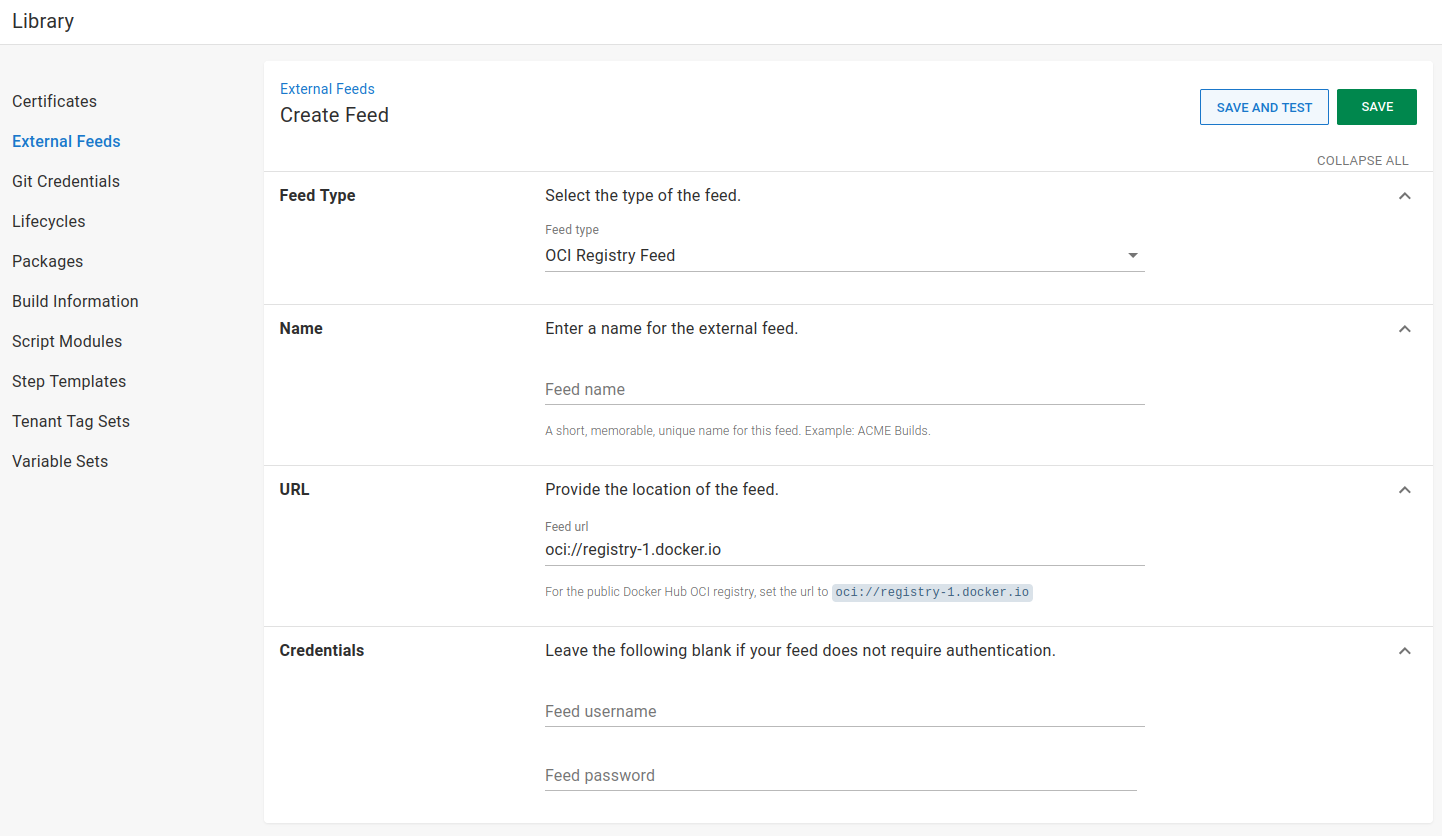
For more information about using OCI-based registries and how to run your own private repository, check out the living documentation on their GitHub repo.
Git repository
Sourcing your Helm charts from a Git Repository can streamline your deployment process by reducing the amount of steps required to get them into Octopus.
To configure a Git Repository source, select the Git Repository option as your Chart Source.
Database projects
If you are storing your project configuration directly in Octopus (i.e. not in a Git repository using the Configuration as code feature), you can source your charts from a Git repository by entering the details of the repository, including:
- URL
- Credentials (either anonymous or selecting a Git credential from the Library)
When creating a Release, you choose the tip of a branch for your Helm charts. The commit hash for this branch is saved to the Release. This means redeploying that release will only ever use that specific commit and not the new tip of the branch.
Version-controlled projects
If you are storing your project configuration in a Git repository using the Configuration as code feature, in addition to the option above, you can source your charts from the same Git repository as your deployment process by selecting Project as the Git repository source. When creating a Release using this option, the commit hash used for your deployment process will also be used to source the chart files.
Helm upgrade step
Since the helm upgrade command provides the ability to ensure that the chart is installed when it runs for the first time (by using the --install argument), this upgrade command is the most practical step to provide.
Remember that since the Kubernetes cluster connection context is available via the kubectl script step, any helm commands that you want to perform that don’t fit into the existing helm upgrade step can easily be scripted as per usual.
Upgrade options
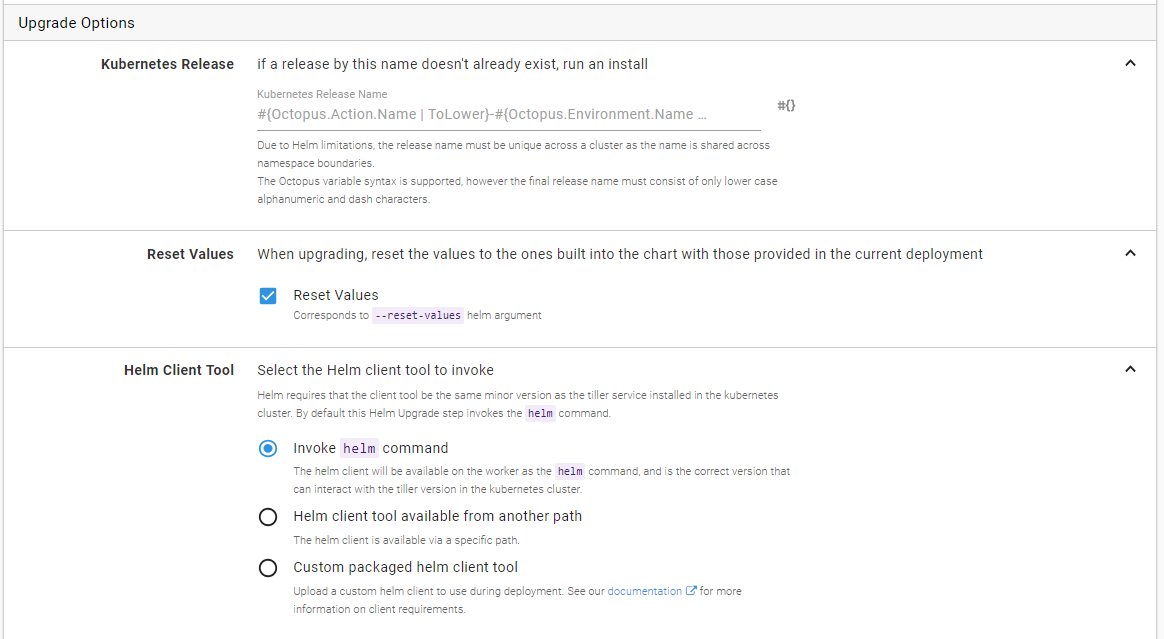
Kubernetes release
The Kubernetes release uniquely identifies the released chart in the cluster. Because of the unique naming requirements of the release name, the default value provided includes both the project and environment name to ensure that successive Octopus releases do not conflict with one another. When redeploying new versions of the chart, this name is what is used to uniquely identify the resources that are related to that Octopus deployment. Helm requires that this name consist of only lowercase alpha numeric and dash (-) characters.
Due to the design of Helm, the release names must be unique across the entire cluster, not just namespaces.
Reset values
By default Helm will carry forward any existing configuration between deployments if not explicitly overridden. To ensure that the Octopus provided configuration acts as the source of truth, the --reset-values argument is set on the invoked command however this can be disabled if desired.
Helm client tool
Helm performs some strict version checks when performing any commands against the cluster and requires that the client have the same minor version as the tiller service (the helm component running in your cluster) in your Kubernetes cluster.
Like the other Kubernetes steps, the Octopus Server or workers will run the Helm commands directly during execution and need to have the helm executable installed.
Since it is quite common to have different versions of Helm across your deployment workers or even across different environments clusters, this option lets you override the helm client tool that is invoked. By default, Octopus will expect the helm command to be directly available to the execution context. Provide either the explicit full path to the desired version of the helm tool or include a version of helm as a package. The available version can be downloaded via the helm public GitHub repository. Unlike some other Octopus steps like Azure Powershell Scripts, the helm client tools are not automatically embedded or installed by Octopus. This is due to the strict version requirements that would differ between Octopus Server installations, and the diverse number of different platform builds available.
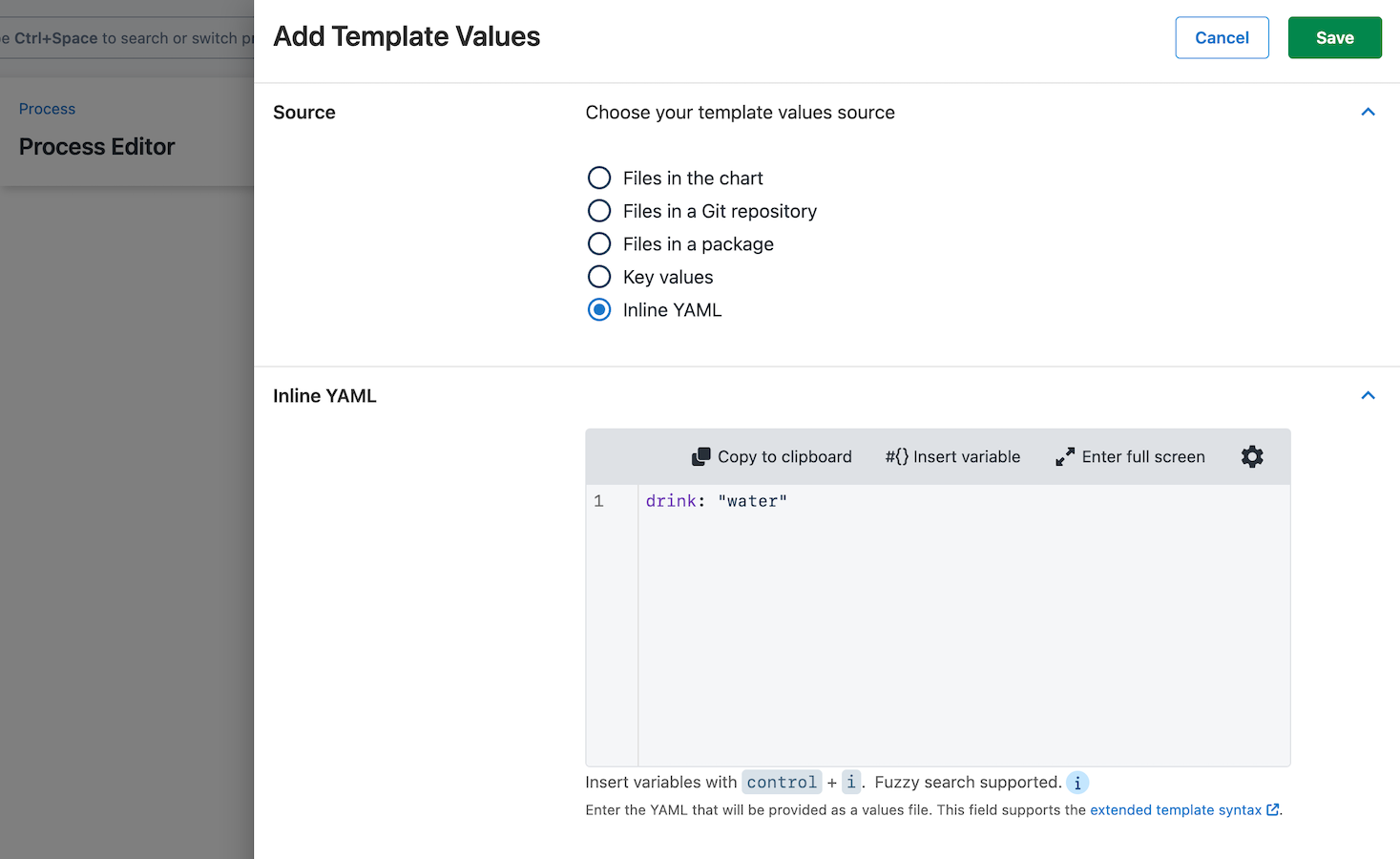
Template values
The configuration for the Kubernetes resources required in a Helm Chart can be provided by making use of Chart Templates. In each of the following options, the values files are passed into the helm upgrade command with the -f argument.
- Files in the chart: If there are any other values files contained within the selected chart (by default,
./values.yamlin the root of the package is picked up by helm), they can be referenced with this option. Octopus Variable replacement will be performed on the file before being used. This works with charts sourced from Packages or Git repositories. - Files in a Git repository: When using publicly available Helm Charts as the package source for this step, you may want to source your custom values files from outside Octopus, for example, through files committed to the Git repository. Files obtained through this option will have Octopus Variable replacement performed before being used.
- Files in a package: When using publicly available Helm Charts as the package source for this step, you may want to source your custom values files from outside Octopus, for example, through files committed to a package repository. Files obtained through this option will have Octopus Variable replacement performed before being used.
- Key values: This option provides the ability to quickly provide key/value pairs of template configuration.
- Inline YAML: Standard Octopus variable substitution syntax can be used so long as the final contents are a valid YAML file.
Except for Files in the chart, you can source template values from the same source type multiple times (e.g. you can source values from multiple different Git repositories).
Reordering values sources
The order of the template values sources dictates the precedence of how the values are applied. Sources are passed in reverse order into the helm upgrade command with the -f argument, which means that sources (and their values) higher in the list have higher precedence and will override the same value in a source with lower precedence. See more information regarding values files precedence in the Helm documentation.
To reorder the sources, click the Reorder button.
In the following figure, the Key values source value for the drink key will take precedence over the value for the same key in the Inline YAML source. The value for the drink key defined in the chart default values.yaml file will be overridden.
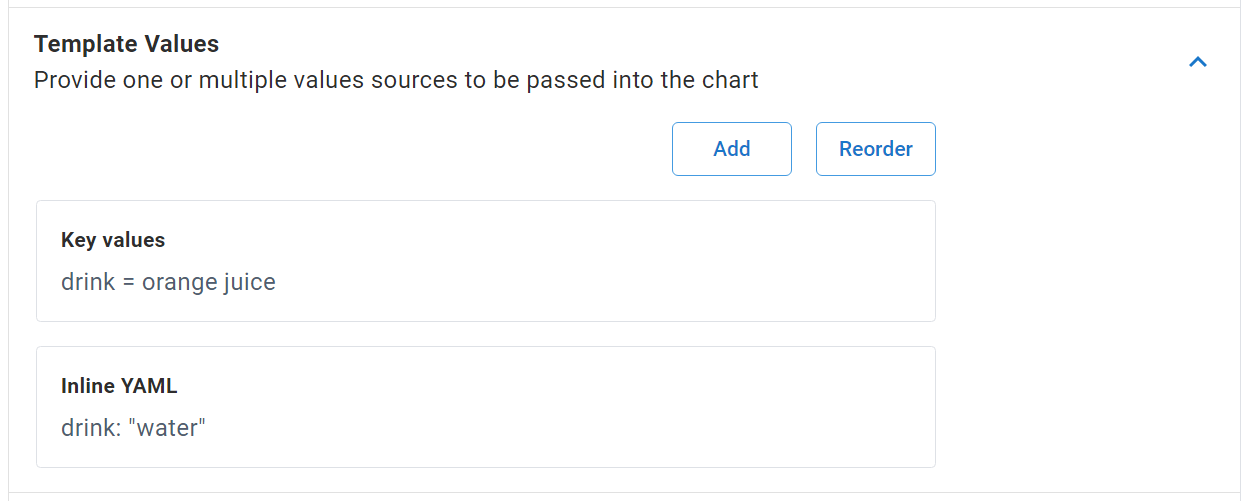
Separating image updates from Helm chart updates
Application updates are often rolled up into full Helm chart version updates because that is the only mechanism provided. When deploying Helm charts with Octopus Deploy, a values file can be used for container image tags so that your Helm charts only get updated when your infrastructure definition changes.
Setting up referenced images with Helm chart deployments
Using this Helm hello-world chart as an example.
For each of the container images referenced by the Helm chart, add a referenced image under Docker image references. The following snippet assumes the referenced package has the Name nginx.
Edit the RAW Values YAML to update the image repository and tag. Take a look inside the example Helm chart to see how they’ve configured their template to use these values.
image:
repository: #{Octopus.Action.Package[nginx].PackageId}
tag: #{Octopus.Action.Package[nginx].PackageVersion}Automatically creating releases
Using referenced images with your Helm chart step allow external feed triggers to automatically create releases when one or more new images are pushed to your registries.
Further to this, lifecycles can be used to fully automate deploying your releases to selected environments.
Known limitations
Please note that Cloud Dynamic Workers come with Helm 2.9.1 installed. This means that if you chose V3 on the Helm Step Template, it will fall back to V2 during execution. To get around this problem, use the Execution Containers feature with the worker tools image.
Helm provides provenance tools that assist in verifying the integrity and origin of a package. Octopus does not currently automatically perform validation checks during a deployment using these tools however this may change in the future.
Although the helm client tool can be overridden for use during the step execution as noted above, the acquisition process currently requires a version of the helm client locally to retrieve the chart. The version of helm available does not need to match the version of the tiller service.
Helm deployments using Tar.gz packages can fail if the path is 100+ characters, to get around this problem use ZIP packages or shorter paths/filenames instead. See https://github.com/OctopusDeploy/Issues/issues/8132 for more info.
Due to how deployment cancellation currently works, the Helm --atomic argument does not result in automatic rollbacks when a deployment is cancelled.
This means that any Helm chart changes that were being deployed may become stuck or only partially deployed, and require manual clean-up.
Furthermore, if the Octopus deployment timeout is set lower than the Helm timeout, a similar issue may arise if the Helm chart deployment is interrupted midway.
To ensure a smooth deployment experience, we recommend setting a larger Octopus timeout than the Helm timeout.
Learn more
Step updates
2024.1:
Upgrade a Helm Chartwas renamed toDeploy a Helm chart.- Support was added for Helm charts stored in Git repositories. You can learn more in this blog post.
2023.3.4127
- Support was added for Helm repositories stored in OCI-based registries.
Help us continuously improve
Please let us know if you have any feedback about this page.
Page updated on Thursday, November 7, 2024