When running Terraform on a local PC, the state of the resources managed by Terraform is saved in a local file. This state is queried to learn which resources already exist in order to properly apply updates and destroy resources.
When Terraform is run by Octopus, this state file is not preserved between executions. This means a remote backend must be configured for almost all practical applications of Terraform through Octopus, allowing the state information to be preserved between Terraform steps.
Refer to the Terraform documentation for more information on configuring backends.
Terraform backends
Neither Octopus nor Terraform will generate errors if a remote backend is not configured, most attempts to update or delete existing resources will not work as expected without a remote backend. We therefore recommend using a remote backend when using terraform with Octopus. You can learn more about storing state remotely here and more general information regarding backends in the Terraform documentation.
Managed cloud accounts
You can optionally prepare the environment that Terraform runs in using the details defined in accounts managed by Octopus. If an account is selected then those credentials do not need to be included in the Terraform template. Using credentials managed by Octopus is optional. These credentials can be saved directly into the Terraform template if that approach is preferable. Credentials defined in the Terraform template take precedence over any credentials defined in the step. The following pages provide instruction on creating cloud accounts:
Remote state Terraform cloud
Using Terraform enterprise for remote state requires a data source using referencing the remote backend
variable "token" {
type = "string"
}
variable "organization" {
type = "string"
}
variable "workspace" {
type = "string"
}
data "terraform_remote_state" "state" {
backend = "remote"
config = {
organization = "${var.organization}"
workspaces = {
name = "${var.workspace}"
}
token = "${var.token}"
}
}As with any other data source, it must exist remotely first. To achieve this, you need an empty template as above which contains only the data source in question. You then need to run terraform init followed by
terraform plan to generate the empty state. The remote state can then be seeded using terraform state push .\.terraform\terraform.tfstate. This is necessary as including resources as part of the template will result in errors such as
No stored state was found for the given workspace in the given backend. as terraform tries to first read the remote state that doesn’t exist.
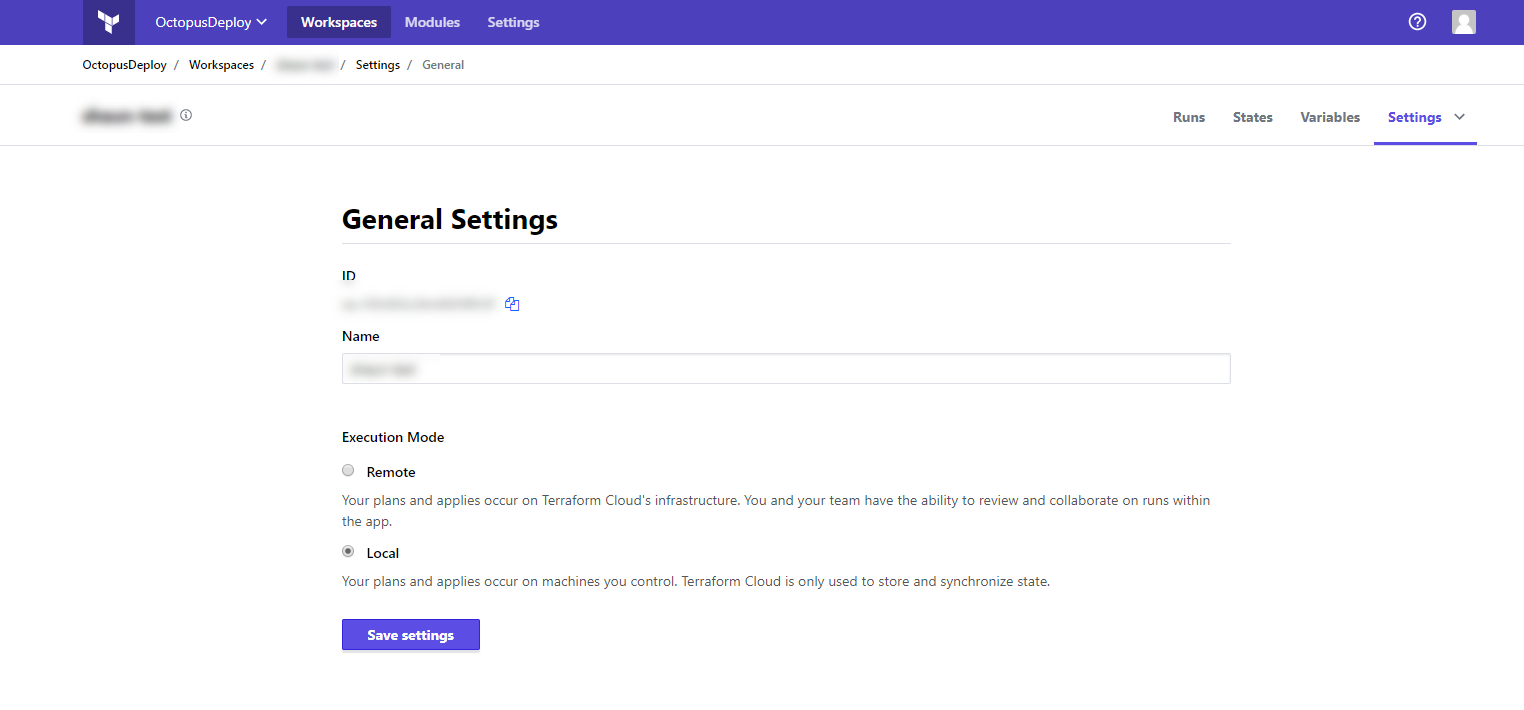
Enhanced backends
Terraform has the concept of enhanced backends which enable both storage and execution of remote operations such as plan and apply. Octopus does not prevent you from using backends such as these, however the execution of actions remotely may not always work as intended. It is for this reason that we recommend using remote state and keep execution of actions local. Terraform Cloud / Enterprise provides an option as part of the workspace settings which makes this rather trivial.
Help us continuously improve
Please let us know if you have any feedback about this page.
Page updated on Wednesday, October 4, 2023